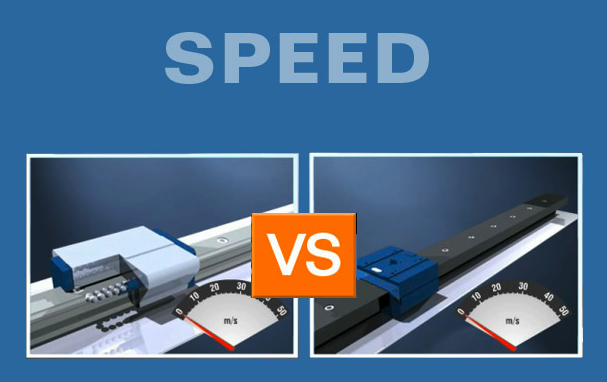
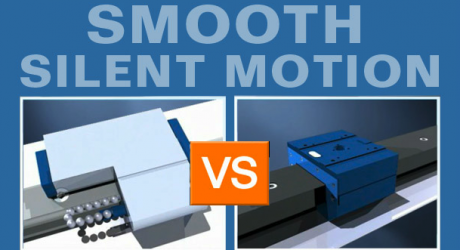
There is an order of magnitude difference which separates the speed capabilities of conventional rolling element bearings from their porous media air bearing counterparts.
Contact with the rail or guideway, and multiple different ball velocities, limit the speed capabilities of conventional rolling element bearings to 3-5 m/s.
Porous media air bearings are a completely non-contact solution. Further, unlike rolling element bearings, their performance is not compromised by any internal moving parts.
This enables porous media air bearings to reach speeds of 30-50 m/s, and to reach such speeds virtually silently.